Access time refers to the amount of time it takes for a computer’s memory to retrieve data and make it available for processing.

Access time refers to the amount of time it takes for a computer’s memory to retrieve data and make it available for processing.

Explore the intricate world of musical accents. Learn “What does accent mean in music?” and its transformative power.
Absorber is device or material that is designed to reduce the amount of sound that is reflected off surfaces in a room, by absorbing the sound waves.

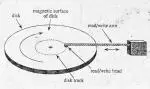
Absolute Time Code also known as A.T.C is specific type of time code that is automatically encoded into the subcode area of a digital tape machine.

A-weighting is a standard for measuring sound levels that takes into account the frequency response of the human ear. This standard is used in many industries, including environmental noise monitoring, industrial hygiene, and workplace safety, to ensure that sound levels are measured and reported accurately.
A-B-X Test is a method of comparing changes in sound quality or components in audio systems, in which three audio sources are used to evaluate whether there is a noticeable difference between two versions of an audio signal.
Absolute phase is a critical component of the sound we hear, yet many people are unaware of its importance. This blog post explains what it is, how it works, and why it matters, providing valuable insights for anyone interested in sound quality.
A-B Stereo is a recording technique. For this you have to use two identical omnidirectional microphones placed some distance apart. A-B stereo microphone technique is often used when the sound source is wide and/or when the distance from the microphones to the source is significant or become somehow relevant in that process of recording.
A-B Repeat refers to that function or option of a hardware or software audio recorders/players that cycles or loops a section of a track.
A-B Comparison refers to the process of switching between two audio sources or parts of a grear / equipment to compare a parameter setting, component, or sound quality. The best A-B comparisons are “blind,” where the listener does not know the identity of the sources until after the test is concluded. The test results are better if the two sources can be switched instantly.

Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is a lossy digital audio compression method, known for delivering sound quality superior to that of its predecessor, MP3. Developed by a consortium of companies, it’s often used in applications where audio quality matters.
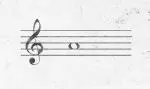
A-440 is a universal standard for musical pitch, whereby the note ‘A’ above middle ‘C’ on a piano, often known as ‘A4,’ is tuned to vibrate at precisely 440 cycles per second, or Hertz (Hz).

As a first definition for “a cappella”, this term refers to a vocal arrangement or a vocal part without instrumental or any kind of accompaniment. In the dj-ing area or remixing jobs the term can also indicate the main vocal part or lead vocal track from the original multitrack recording which can be used as the basis for a whole new edit.
Also called “Post Fade Listen”, AFL (After Fade Listen) is the feature that comes within the pro mixing desks / consoles which gives to sound engineers or artists the possibility of monitoring one or more specific signals / tracks alt the same level set by the fader of level control knob. Aux Sends are mostly monitored AFL.
An Analog to Digital Converter is one of the most used devices in today music production industry since the computers are the core of today recording and production studios.
AIFF is the abbreviation for Audio Interchange File Format. The term “AIFF” refers to that audio file format standard developed by Apple in 1988 after Electronic Arts Interchange File Format known as IFF.
