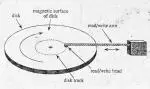
In almost all cases, Access Time refers to that time a disk, an optical disk or an hard disk needed for reach or read a data sector.
There are a lot of factors that are involved in definition of access time. The physical speed of the hardware, the delay or the amount of time the hardware need for finding the data sector, the buffer and so on.
In everything that involves music production and also in the video production, lower access time numbers are better because a huge amount of data is needed to be reached fast.
What is Access Time: Table of Contents
Access time is a crucial factor in determining how efficiently your computing system operates. It refers to the time it takes for your computer’s memory or storage devices to retrieve and make available the data necessary to perform a specific task. Slow access times can lead to sluggish system performance, negatively affecting your user experience and potentially harming your business productivity. In this blog post, we will take an in-depth look at access time, its different types, importance, and techniques for measuring and optimizing it.
Types of Access Time
There are three primary types of access time: memory access time, disk access time, and network access time. Let’s dive into each one to understand its definition, factors affecting it, and techniques for improving it.
Memory Access Time
Memory access time refers to the time it takes for a computer’s processor to access data stored in its memory. There are two main types of memory: random-access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM). RAM is a volatile memory type that stores data temporarily and allows for quick access by the processor. ROM, on the other hand, is a non-volatile memory type that stores data permanently and cannot be modified by the processor.
Factors affecting memory access time include the type and speed of memory, processor speed, cache memory size, and system bus speed. To improve memory access time, you can upgrade your memory modules, reduce the number of background processes running, and utilize caching techniques to store frequently accessed data in a faster memory location.
Disk Access Time
Disk access time refers to the time it takes for a storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, to retrieve data from its storage media. Factors affecting disk access time include the type and speed of the disk drive, the rotational speed of the disk platters, the seek time required for the read/write head to locate the data, and the transfer rate at which data can be read from or written to the disk.
To improve disk access time, you can utilize disk defragmentation to optimize the location of data on the disk, upgrade to a faster disk drive or solid-state drive, and utilize RAID (redundant array of independent disks) technology to increase data transfer rates and fault tolerance.
Network Access Time
Network access time refers to the time it takes for a computer to send and receive data over a network connection. Factors affecting network access time include the speed and reliability of the network connection, the distance between the client and server, the type of network protocol being used, and the amount of network traffic.
To improve network access time, you can upgrade to a faster network connection, reduce network congestion by optimizing network traffic, and utilize caching techniques to store frequently accessed data locally.
Importance of Access Time
Access time is a critical factor in determining how efficiently your computing system operates. Slow access times can lead to poor system performance, negatively impacting your user experience and potentially harming your business productivity. Here are some of the key reasons why access time is important:
- Impact on System Performance: Slow access times can cause your system to become unresponsive, leading to delays and potential crashes. Optimizing access time can significantly improve system performance, allowing you to work faster and more efficiently.
- User Experience and Perception: Users expect fast and responsive systems. Slow access times can negatively impact user satisfaction, leading to frustration and potential loss of business.
- Implications for Business and Industry: In business and industry, slow access times can have significant financial implications, leading to lost productivity and revenue. Optimizing access time can help reduce operational costs and increase competitiveness.
Measuring Access Time
Measuring access time is crucial to understanding your system’s performance and identifying areas for improvement. There are several techniques for measuring access time, including:
- Benchmarking Tools: Benchmarking tools, such as CrystalDiskMark and ATTO Disk Benchmark, can provide detailed measurements of disk read and write speeds, helping you identify potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- System Monitoring Tools: System monitoring tools, such as Task Manager and Resource Monitor, can provide real-time measurements of system performance, including memory and disk usage, CPU utilization, and network traffic.
- Network Performance Tools: Network performance tools, such as Ping and Traceroute, can help you measure network latency and identify potential network connectivity issues.
Optimizing Access Time
Optimizing access time requires a holistic approach, addressing all aspects of your system that may be impacting performance. Here are some techniques for optimizing access time:
- Upgrade Memory: Upgrading your memory modules can significantly improve memory access time, allowing your processor to quickly access frequently used data.
- Utilize Caching Techniques: Caching techniques, such as read-ahead caching and write-behind caching, can help reduce disk access time by storing frequently accessed data in a faster memory location.
- Optimize Disk Usage: Optimizing disk usage through disk defragmentation and file compression can improve disk access time by reducing seek times and optimizing the location of data on the disk.
- Utilize RAID Technology: RAID technology can improve disk access time by increasing data transfer rates and providing fault tolerance, ensuring that your data remains accessible even in the event of a disk failure.
- Upgrade Network Connection: Upgrading to a faster network connection can significantly reduce network access time, allowing for faster data transfer rates and improved connectivity.